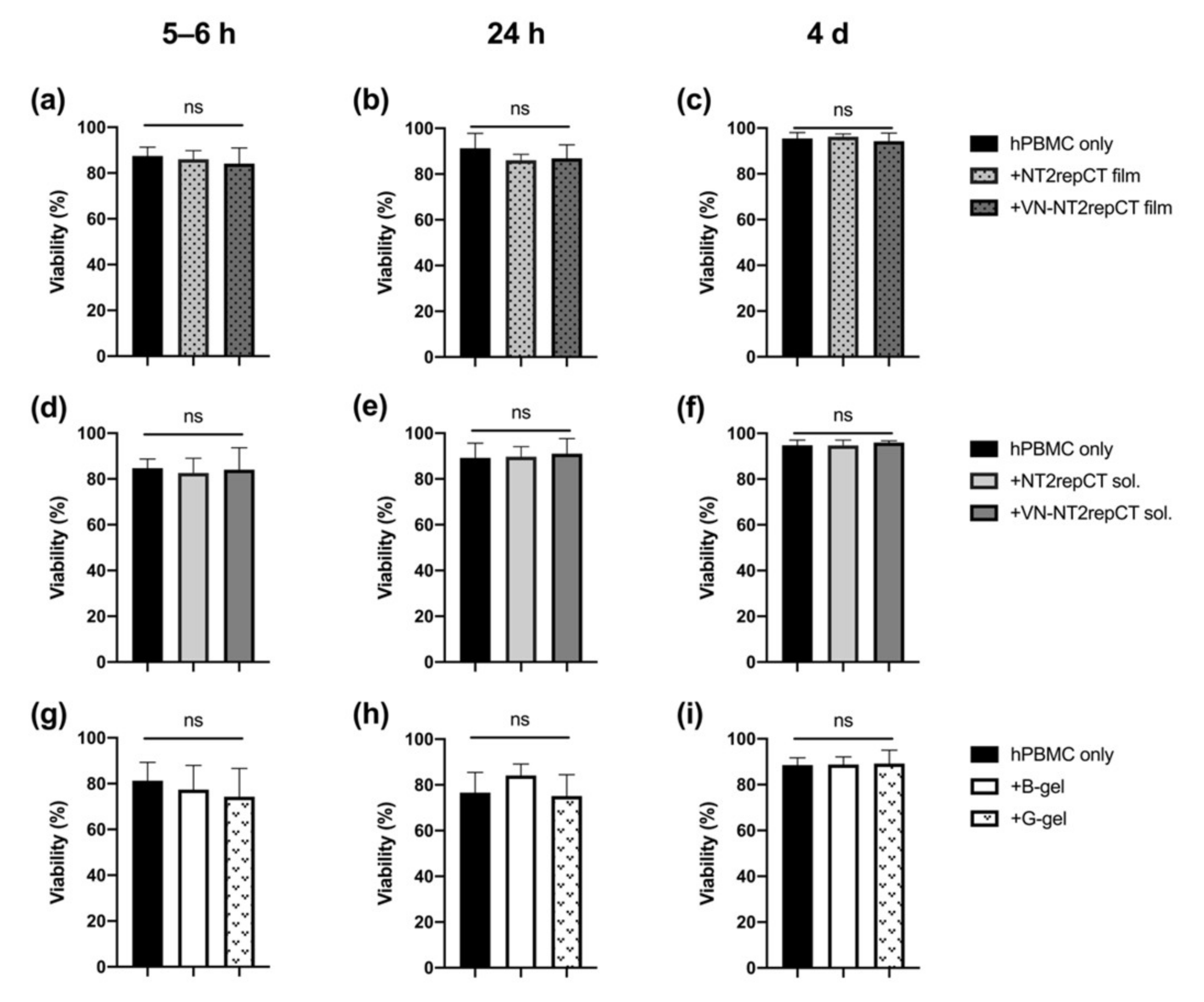
Peripherally Delivered Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase Gene Therapy for Spinal Cord Injury Pain: Molecular Therapy

Motor and somatosensory degenerative myelopathy responsive to pantothenic acid in piglets - Marina P. Lorenzett, Aníbal G. Armién, Luan C. Henker, Claiton I. Schwertz, Raquel A. S. Cruz, Welden Panziera, Claudio S. L.

Could adding folic acid to salt curb Ethiopia's sky-high rate of spinal cord deformities? | Science | AAAS
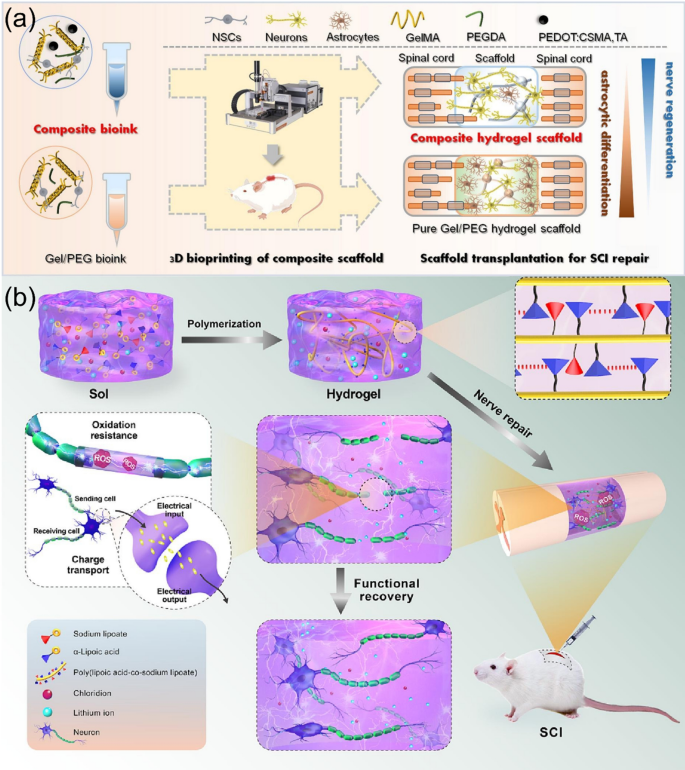
Recent advance in bioactive hydrogels for repairing spinal cord injury: material design, biofunctional regulation, and applications | Journal of Nanobiotechnology | Full Text

Activation of Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor Type 1 Contributes to Pathophysiology of Spinal Cord Injury | Journal of Neuroscience

Distinct Glycosylation Responses to Spinal Cord Injury in Regenerative and Nonregenerative Models | Journal of Proteome Research

Histopathology of spinal cord. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of spinal... | Download Scientific Diagram

Journal of Neurosurgery on X: "#FreeArticle: Hyaluronic acid scaffold has a neuroprotective effect in hemisection spinal cord injury https://t.co/m44TMutg6b https://t.co/EgPwsgX4oU" / X
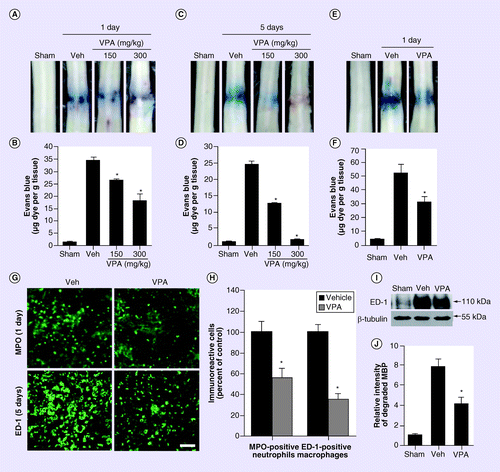
Valproic acid-mediated neuroprotection and neurogenesis after spinal cord injury: from mechanism to clinical potential | Regenerative Medicine

Expression of the main components of the retinoic acid (RA) signaling... | Download Scientific Diagram

New orally available drug for spinal cord injury found to be safe and tolerable in healthy participants - King's College London

Activation of Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor Type 1 Contributes to Pathophysiology of Spinal Cord Injury | Journal of Neuroscience

Preliminary Study on the Fabrication of Alginate/Hyaluronic Acid Scaffolds for Spinal Cord Injury Repair | Semantic Scholar

Polysialic-Acid-Based Micelles Promote Neural Regeneration in Spinal Cord Injury Therapy | Nano Letters

A tannic acid doped hydrogel with small extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells promotes spinal cord repair by regulating reactive oxygen species microenvironment - ScienceDirect

Injectable Porous Scaffolds Promote Better, Quicker Healing After Spinal Cord Injuries - AIP Publishing LLC
Recovery of Amino Acid Neurotransmitters from the Spinal Cord During Posterior Epidural Stimulation: A Preliminary Study: The Journal of The American Paraplegia Society: Vol 14, No 1